
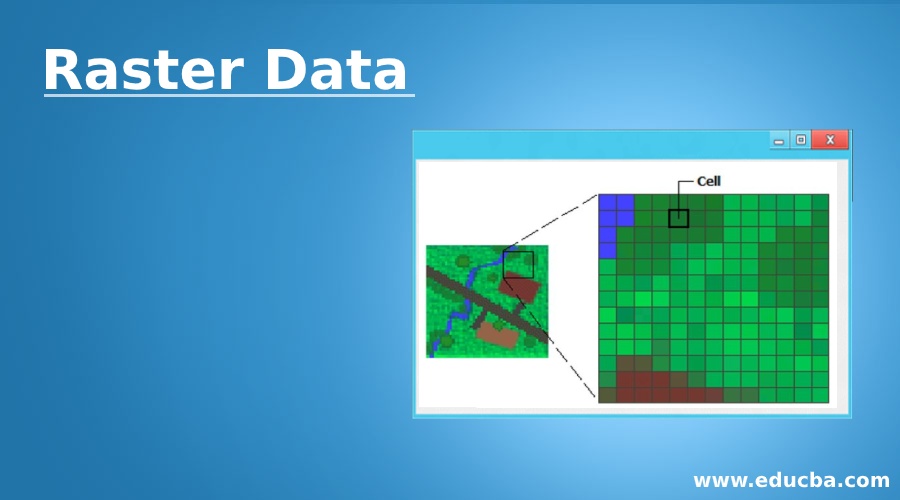
In the example at right, the cells of tessellation A are overlaid on the point pattern B resulting in an array C of quadrant counts representing the number of points in each cell. The most common way to do this is a row-major format, in which the cells along the first (usually top) row are listed left to right, followed immediately by those of the second row, and so on. To store the data in a file, the two-dimensional array must be serialized. A raster data structure is based on a (usually rectangular, square-based) tessellation of the 2D plane into cells, each containing a single value. Most computer images are stored in raster graphics formats or compressed variations, including GIF, JPEG, and PNG, which are popular on the World Wide Web. Using a raster to summarize a point pattern. The digital sensors used for remote sensing and astronomy are often able to detect and store wavelengths beyond the visible spectrum the large CCD bitmapped sensor at the Vera C. Rubin Observatory captures 3.2 gigapixels in a single image (6.4 GB raw), over six color channels which exceed the spectral range of human color vision.Īpplications Image storage Most modern color raster formats represent color using 24 bits (over 16 million distinct colors), with 8 bits (values 0–255) for each color channel (red, green, and blue).
#DEFINE RASTER FULL#
Common pixel formats are binary, gray-scale, palettized, and full-color, where color depth determines the fidelity of the colors represented, and color space determines the range of color coverage (which is often less than the full range of human color vision). Each raster grid has a specified pixel format, the data type for each number. For most images, this value is a visible color, but other measurements are possible, even numeric codes for qualitative categories. Raster or gridded data may be the result of a gridding procedure.Ī single numeric value is then stored for each pixel. The size of each square pixel, known as the resolution or support, is constant across the grid. In digital photography, the plane is the visual field as projected onto the image sensor in computer art, the plane is a virtual canvas in geographic information systems, the plane is a projection of the Earth's surface. For example, a large bitmap image saved in the lossy JPEG format will have a smaller file size than the same bitmap image saved as a losslessly-compressed PNG file, which in turn will be smaller than that image saved as an uncompressed BMP file.The fundamental strategy underlying the raster data model is the tessellation of a plane, into a two-dimensional array of squares, each called a cell or pixel (from "picture element"). NOTE: There are many file formats used for raster graphics, some of which include image compression to reduce file size. Scaling one up requires creating new data between the existing pixels, which can result in an image that's either blurry or blocky.
Shrinking one down requires the data from multiple pixels to be combined, causing fine details to be lost. Since raster graphics consist of a grid of pixels, resizing one to change its resolution will necessarily change the contents of those pixels. An image with 24 bits of color depth uses three times as much data but can use more than 16 million colors. An image with 8 bits of color depth can only display 256 colors. A raster graphic's file size also depends on its color depth - how many bits of data each pixel requires.
For example, an image 640 pixels wide by 480 pixels tall consists of 307,200 pixels total, while a larger 3072 x 2048 image requires 6,291,456 pixels.
A higher-resolution image has more pixels and thus requires more disk space to store.

The first is a raster graphic's image size, also known as its resolution - the number of pixels it is wide by the number of pixels it is tall. The file size of a raster graphic depends on several variables. They are one of the two primary image types for computer graphics with vector graphics. Most images on the Internet and your computer are raster graphics. Raster graphics are computer graphics that consist of a grid of pixels, also known as a bitmap.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
